 Central Minnesota is a manufacturing stronghold, with several global manufacturing firms operating there.
Central Minnesota is a manufacturing stronghold, with several global manufacturing firms operating there.
The region is especially well known for its expertise in food processing, printing, furniture manufacturing, appliances, machinery and heavy equipment manufacturing.
View our latest blogs on CareerForce. Want the freshest data delivered by email? Subscribe to our regional newsletters.
3/31/2025 11:54:03 AM
Luke Greiner
Employment data shows that Central Minnesota has demonstrated economic resilience amid recessions, benefiting from geographic advantages while also facing industry-specific challenges. Unlike some other regions, Central Minnesota experienced job growth during certain downturns, even as key industries like Manufacturing and Retail Trade saw significant job losses.
Economic Trends During Past Recessions
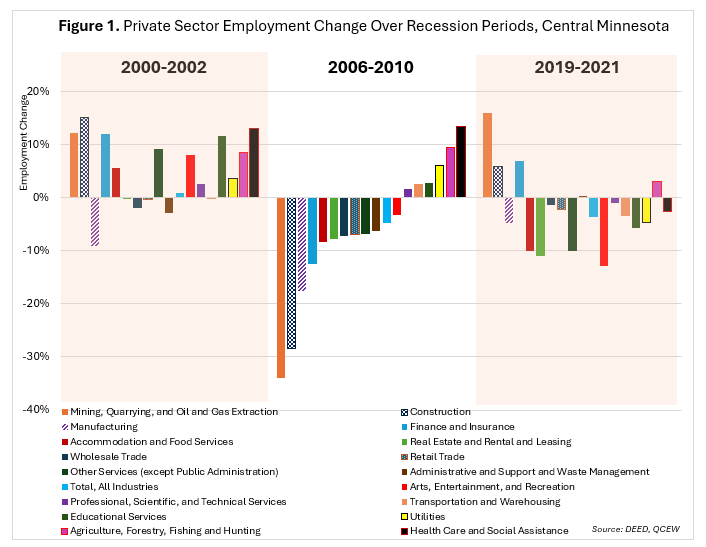
During the early 2000's recession, Central Minnesota's economy showed mixed employment results. While Manufacturing shed 9% of its workforce from 2000 to 2002, resulting in 4,200 lost jobs, these declines were offset by substantial growth in Health Care & Social Assistance (+13%), Construction (+15%) and Finance & Insurance (+12%). Interestingly, the region thrived with a 17% job gain at Specialty Trade Contractors and Food & Drinking Places expanded by 8% as the region's population continued increasing.
The Great Recession in 2008, however, brought more severe job losses. Construction and Manufacturing were hit hardest, losing 30% and 18% of jobs, respectively, from 2006 to 2010. The combined loss of nearly 12,500 jobs in these sectors accounted for the majority of Central Minnesota's overall employment decline during this time frame. Retail Trade and Accommodation & Food Services also suffered, while industries like Warehousing (+128%) and Chemical Manufacturing (+28%) saw unexpected growth. Health Care remained a beacon of stability in the region, growing 17% and reinforcing its reputation as a recession-proof industry (see Figure 1).
The Pandemic Recession's Unique Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic created a different economic shock, with strict lockdowns leading to employment declines in traditionally stable industries. Health Care & Social Assistance, usually recession-resistant, lost nearly 800 jobs from 2019 to 2021. Manufacturing declined by 5%, while the hardest-hit sectors were Arts, Entertainment & Recreation (-13%), Accommodation & Food Services (-10%), Other Services (-10%), and Real Estate, Rental & Leasing (-11%). Meanwhile, industries like Internet Services (+54%) and Courier Services (+25%) saw rapid expansion due to shifting consumer demands.
Recession-Resistant Industries
Despite economic downturns, some sectors have consistently added jobs. For example, Agriculture, Health & Personal Care Stores and Ambulatory Health Services have grown in Central Minnesota through multiple recessions. Understanding these resilient industries can guide workforce development strategies to ensure long-term economic stability in Central Minnesota.
For more information about employment trends in Central Minnesota, contact Luke Greiner at luke.greiner@state.mn.us.